Mar 16 2023
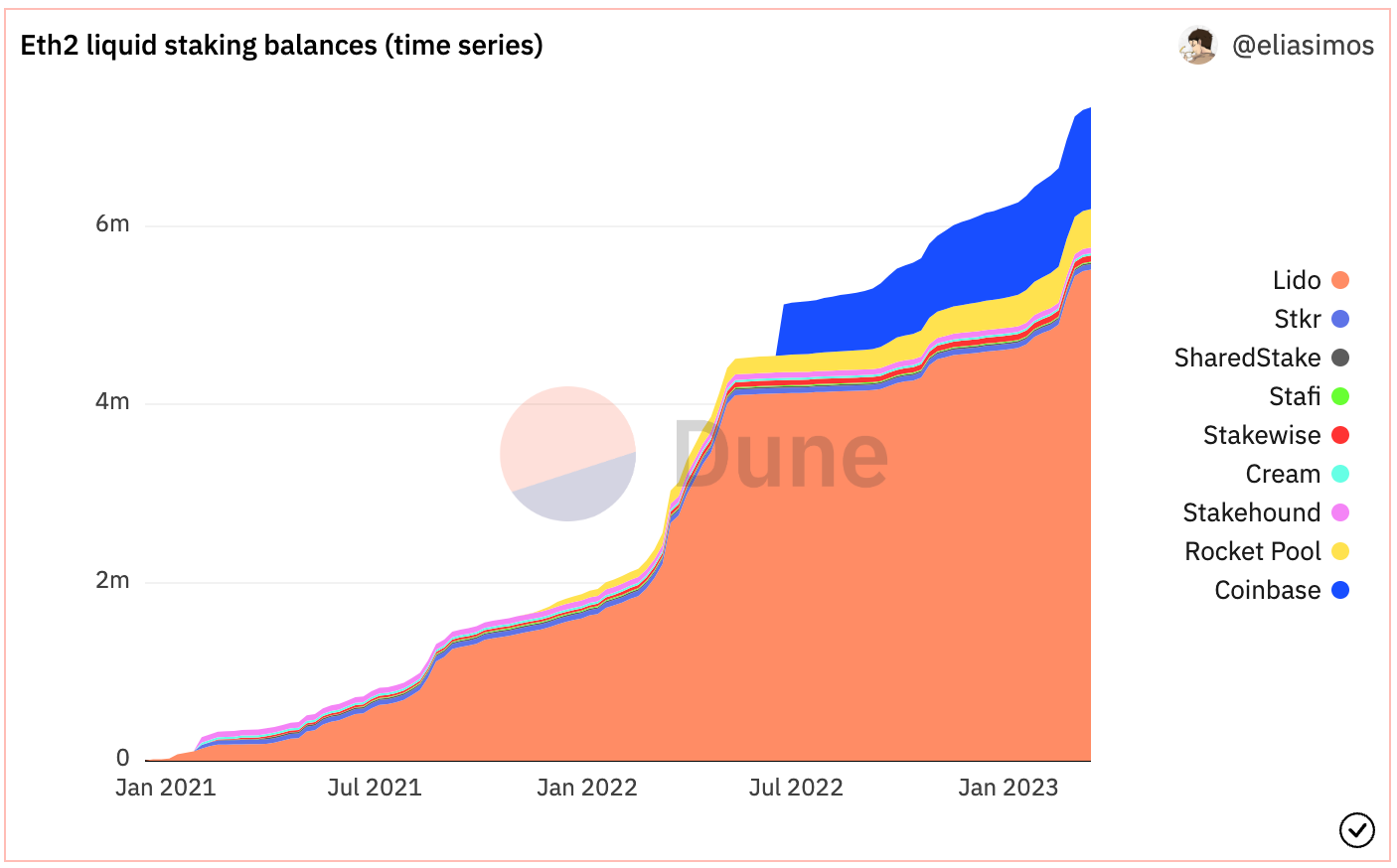
As the crypto and decentralized finance (DeFi) industry continues to mature, liquid staking has emerged as a solution attracting the attention of both retail and institutional participants.
Liquid staking allows participants to directly stake their tokens, which will accrue network rewards, and retain the ability to transfer or use their staked tokens in DeFi via a Liquid Staking Token (LST). When a participant stakes their tokens via the Liquid Collective protocol, the protocol programmatically generates and mints LSTs to represent the participant's legal and beneficial ownership of its staked tokens and the network rewards that accrue to the tokens. LSTs provide flexibility, liquidity, and capital efficiency for participants, which we believe improves the staking experience.
Growing adoption of crypto by institutional investors has long been cited as a meaningful channel for growth of the web3 ecosystem overall. According to research published by Fidelity Digital Assets in Q4 of 2022, surveying institutional investors in the U.S. and Europe, 74% of institutions are planning to buy digital assets in the future and 51% have a positive perception of digital assets, which represents a percentage that has continued to increase year over year.
Institutional adoption applies to staking as well. According to reporting from Cointelegraph, Coinbase CEO Alesia Haas noted in the company's Q2 '22 earnings call “that institutional staking of crypto assets could be a 'phenomenon' in the future as soon as the market overcomes its liquidity lock-up.”
We believe liquid staking is an important technological innovation representing the industry's answer to staking's liquidity constraints. However, despite the growing popularity of liquid staking, we see several challenges that have hindered institutions from participating in a widespread and meaningful way. For example, we believe compliance is the main concern for institutions, which require a level of transparency and due diligence that we believe most existing liquid staking options don't offer.
Potential blockers to institutional participation in liquid staking
Institutions are generally subject to a wide range of regulatory requirements and compliance standards.
One key area of compliance for institutions is counterparty risk, or the risk that one party in a financial transaction will fail to meet its obligations, leaving the other party with losses. Institutions are required to manage counterparty risk, which may entail abiding by processes to assess the creditworthiness and reputation of their counterparties. This involves performing due diligence checks and implementing measures to prevent fraud and other types of financial crimes.
Another important area of compliance for institutions is KYC/KYB/AML, or regulatory requirements for 'know your customer,' 'know your business,' and 'anti-money laundering' and sanctions processes that aim to prevent financial crimes like money laundering and terrorist financing. KYC/KYB/AML regulations require institutions to verify the identities of their customers and counterparties, as well as to assess the risks associated with these relationships to avoid inadvertently facilitating financial crimes.
Failure to comply with these regulations can result in civil or criminal liability, financial losses, and damage to institutions' reputations. In addition, certain institutional investors may prefer or be required to custody their digital assets through a qualified custodian. We understand that institutions also typically prefer the ability to access deep liquidity in order to facilitate their large-sized trades when necessary.
In general, we believe many actively managed and decentralized liquid staking solutions present significant barriers to institutional participation.
Certain features of actively managed offerings:
- Pose centralization risks, and may lack transparency into the staking process
- Offer LSTs with limited interoperability or composability
- May have fragmented liquidity due to competing standards
Certain features of decentralized offerings:
- May lack counterparty compliance with no KYC/AML performed on Node Operators supporting the protocol's active set, Platforms, or users
- May lack validator performance and security standards, or may lack transparency into those standards
- May have consumer-facing product and commercial designs inadequate for B2B integrations
The Liquid Collective protocol was developed to unlock institutional participation in decentralized liquid staking, without sacrificing enterprise-grade features.
Liquid Collective: the enterprise-grade liquid staking standard
Liquid Collective is a decentralized liquid staking protocol that aims to provide an enterprise-grade liquid staking standard for the entire web3 ecosystem. The Liquid Collective protocol is a liquid staking protocol designed to empower global participation in securing the decentralized internet by solving for certain blockers to institutional participation in staking, including the need for KYC/AML compliance and sanctions screening.
At its core, the Liquid Collective protocol is software code that enables users to stake directly via the Ethereum blockchain. The staking and LST or “receipt token” processes occur transparently onchain, according to pre-programmed code. Liquid Collective comprises an ecosystem of software components and service providers, including Platforms that serve as on-ramps to the Liquid Collective protocol, conduct KYC review, and submit whitelisted user addresses. Unaffiliated third party Node Operators—who may even comprise commercial competitors—operate the validators' nodes independently of any one centralized intermediary.
The protocol's LST for Ethereum is Liquid Staked ETH (LsETH). Each unit of LsETH is a digital certificate of title that evidences the holder's legal and beneficial ownership of the holder's staked ETH and any network rewards that accrue to the staked ETH. Ownership of the staker's ETH never passes to any third party. Because the Liquid Collective protocol is non-custodial and does not control users' tokens, the protocol doesn't decide when and how many tokens to stake. Instead, all staking actions are controlled by the staker.
The LsETH User Agreement is a form of customer-facing documentation that addresses, among others, LsETH's specifications, participants' legal and beneficial ownership of staked ETH, fees, risks of participation, and disclaimers. Specifically, the agreement details the protocol's Service Fee and the Ethereum network's withdrawal restrictions (e.g., unbonding period). The LsETH User Agreement also covers the protocol's Slashing Coverage Program.
While the protocol is designed to meet deep institutional liquidity needs across the protocol's Platforms' venues, the Liquid Collective protocol does not maintain a “liquidity reserve,” nor does it promote or offer instant liquidity, regular investment payouts, or tout specified investment returns. All network rewards are determined by the Ethereum network instead of a centralized intermediary, and the network has complete discretion over the amount of the network rewards generated by staked tokens. Moreover, then network determines the distribution and payout schedule of network rewards that accrue to staked tokens. As a decentralized liquid staking solution, the Liquid Collective protocol utilizes software code to offer liquid staking in accordance with the parameters of the Ethereum network.
Overall, the Liquid Collective protocol is thoughtfully designed to provide a tool for stakers to directly stake on the Ethereum network, with access to liquidity via LsETH, and offering certain compliance and security measures for institutions.

Compliance: The Liquid Collective protocol requires KYC/KYB/AML for users and operators, which aims to facilitate compliance and mitigate the risk of sanctions screening. This is important for institutions who have strict regulatory requirements and need to comply with due diligence standards to protect themselves from reputational harm and business disruptions.
To facilitate this compliance, Exiger, a premier software and tech-enabled governance, risk, compliance and diligence solutions firm, conducts the protocol's compliance program reviews, AI-enabled open-source screening, and due diligence of participants, in addition to the KYC/AML checks completed by Platforms when onboarding users to stake via the protocol.
Validators: The Liquid Collective protocol is connected with an enterprise-grade validator set, and Ethereum network rewards are generated by a distributed set of security-focused infrastructure providers. Stake on the protocol is distributed in a round-robin manner amongst a distributed group of node operators that employ multi-cloud, multi-region and multi-client infrastructure.
Built for enterprise participants: The Liquid Collective protocol's API-first solution provides a frictionless onboarding path for Platforms.
Collaborative, decentralized approach: Liquid Collective's mission to empower global participation in securing the decentralized web involves collaborating with proven industry participants, including trading venues, custodians, service providers, and node operators, to build a performant liquid staking standard. This concept of decentralization through collective collaboration is core to the Liquid Collective protocol's design, and offers a decentralized path for institutions to directly participate in liquid staking, which we believe will help preserve and improve the proof of stake ecosystem's decentralization overall.
The Liquid Collective protocol is open source and governed by a broad and dispersed community of leading web3 teams via the Liquid Collective protocol's governance framework. Liquid Collective's protocol governance may evolve over time as the community submits and votes to accept governance proposals.
Moving forward
The lack of regulatory clarity surrounding liquid staking has long been cited as a primary barrier to liquid staking's widespread adoption and development. Despite this lack of clarity, responsible protocols like Liquid Collective aim to meet the compliance needs of participants, while taking part in industry efforts to develop best practices, advocate, and self-regulate to protect users' safety and continue driving liquid staking's responsible growth. Liquid Collective is proud to support the work of the Proof of Stake Alliance in their efforts advocating for forward-thinking public policies surrounding staking in the US and globally.
With Liquid Collective, institutional participants can reasonably participate in staking while meeting their compliance requirements and not sacrificing liquidity. This has the potential to drive widespread participation in securing the decentralized web.




